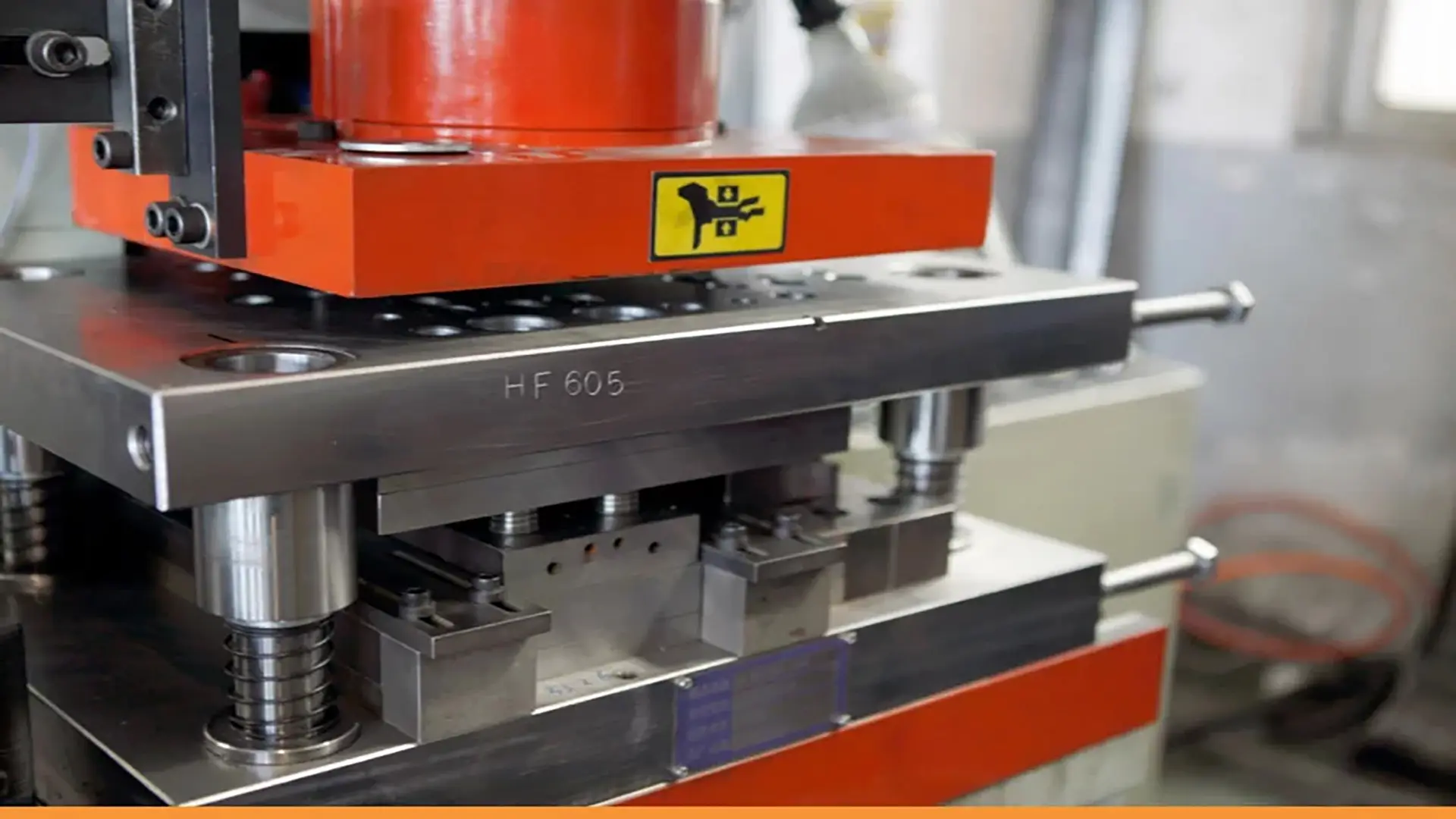

Dies are important tools in industrial production processes. They can be classified based on their constituent components, design, and the number of workstations. This section will briefly discuss the classification of dies based on the number of workstations.
1. Single-Station Dies
These types of dies have only one workstation where the forming process takes place. In single-station dies, various operations such as cutting or bending may be performed in a single stage (press stroke). These dies are divided into two categories: Compound Die: In these dies, several different operations, such as cutting and bending, are performed to produce a single part in one press stroke. Combination Die: These types of dies combine cutting and non-cutting processes, which are used in a single press stroke to produce the desired part. For example, in a combination die, a cutting operation might be performed first, followed by bending or forming on the part.
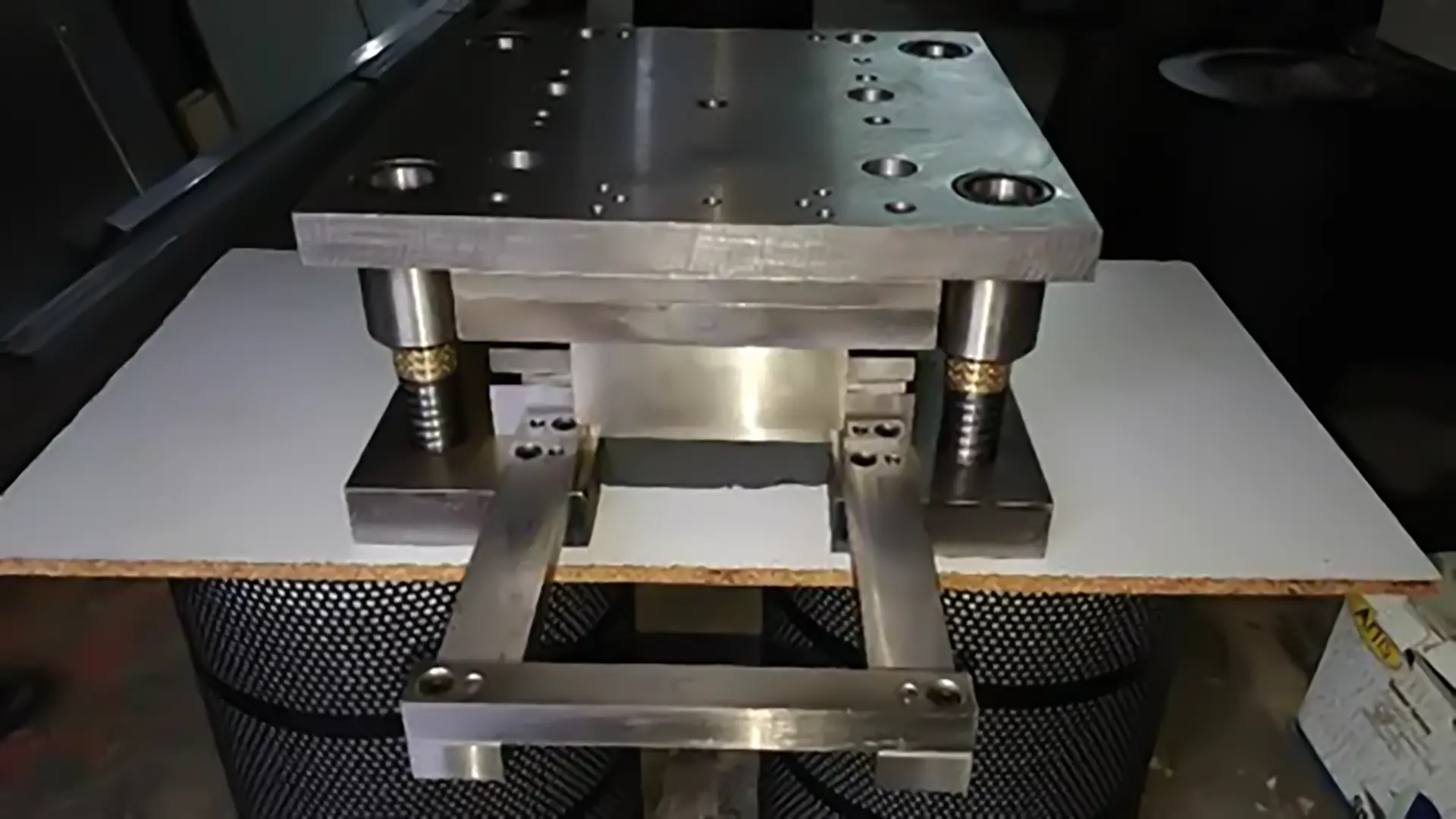
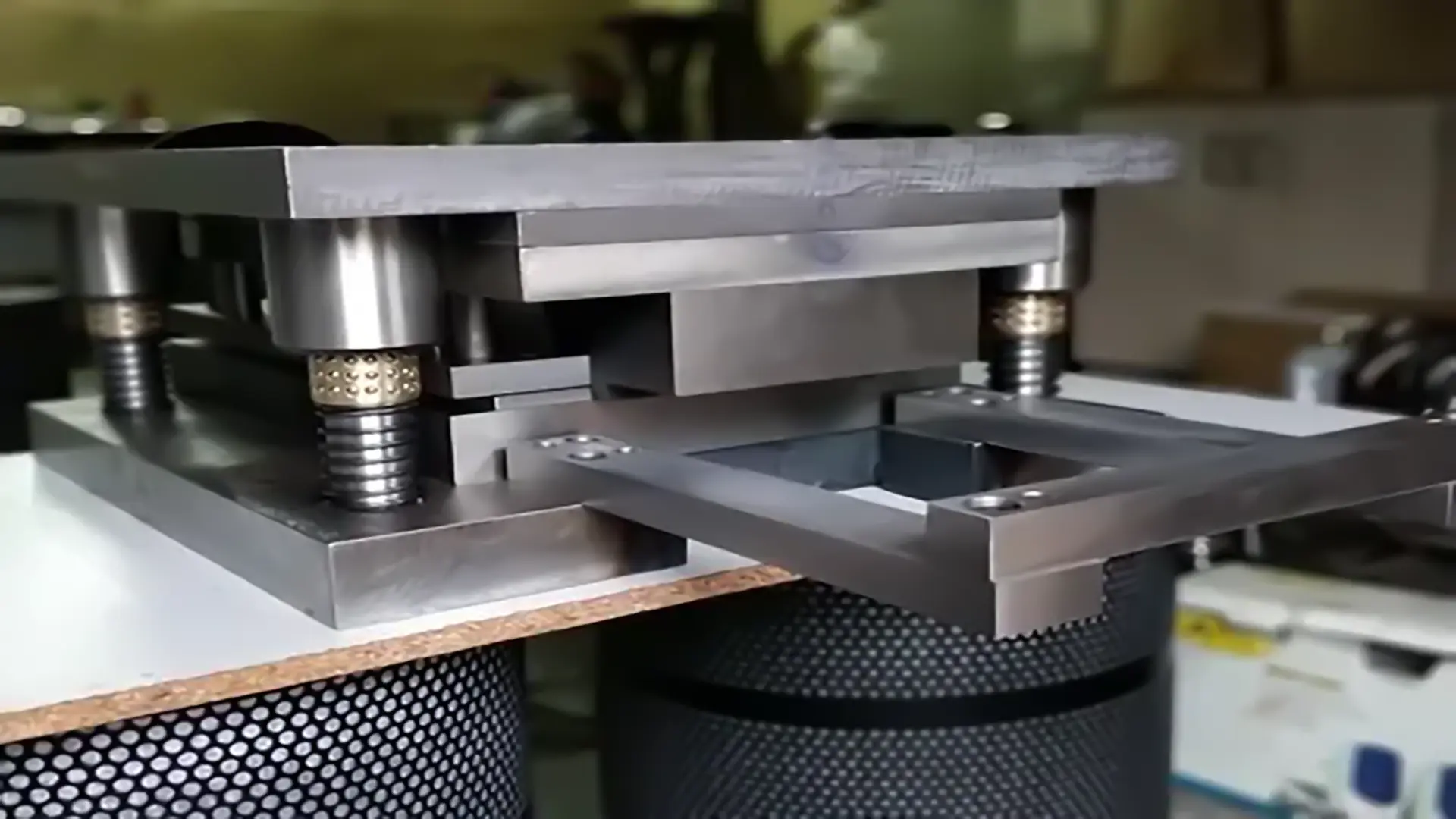

2. Multi-Station Dies
These dies include multiple workstations, each performing a part of the part production process, and are divided into two categories: a. Progressive Dies In these dies, a strip of sheet metal moves continuously from one station to the next, undergoing operations such as cutting, bending, or drawing. Finally, the finished part is separated from the strip. For higher precision, locating pins and specialized feeders are used. b. Transfer Dies In this type, the blank is transferred from one station to the next by a transfer mechanism. For large parts, tandem press lines are used, which move the part between multiple presses. Advantages of Multi-Station Dies: High precision in executing different stages. Increased production speed. Cost reduction by eliminating the need for separate dies.
Conclusion
The choice of die type depends on the type of process and the characteristics of the desired part. Single-station dies are suitable for simpler parts and faster processes, while multi-station dies are used for more complex parts and the need for high precision in various production stages. The correct choice of die can significantly impact the final product quality and reduce production costs.
