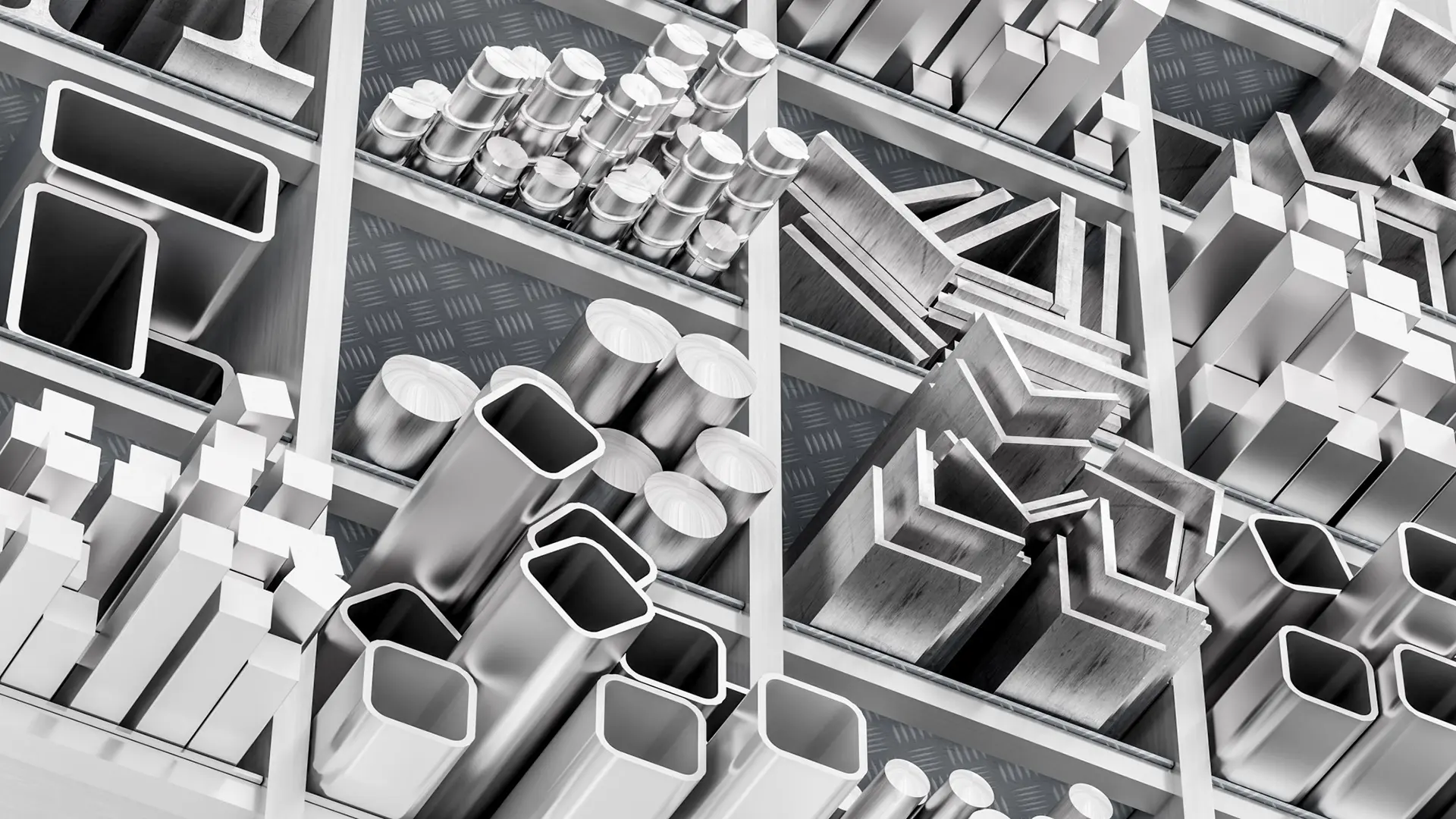
Extrusion is a manufacturing process in which metal or other materials are forced under pressure through dies with a smaller cross-section. This operation is recognized as one of the advanced methods for shaping and producing parts with complex cross-sections. The deformed material resulting from this process is typically known as the “extrudate”. The main advantage of this method is the ability to produce complex profiles and the capability to use brittle materials that might not be usable in other production methods.
Types of extrudable materials
Extrusion is not limited to metals and can be applied to various types of materials. In addition to metals, polymers, concrete, ceramics, and other materials are also subjected to the extrusion process. In this method, the material is usually subjected to pressure either cold or hot, depending on its properties and production requirements.


Extrusion process
The extrusion operation is carried out using an extruder machine. This machine uses a piston to force the workpiece into the chamber. Inside the extruder, the piston applies pressure to the workpiece, causing it to pass through the die with a specific cross-section. Due to pressure and friction, heat is generated in the material; therefore, a cooling system is needed to prevent the material from overheating.
Extrusion methods
Direct Extrusion Method In this method, the ram (piston) and the billet (workpiece) move in the same direction. This means the container (chamber) is stationary, and the billet is pushed into it under pressure. This method is relatively simple and is typically used for producing long parts with a constant cross-section. Indirect Extrusion Method In this method, the die moves relative to the stationary billet (or the billet is pushed through the die without moving relative to the container walls). This means the billet remains stationary relative to the container, and the die assembly moves towards the billet, forcing the material through the die opening. Less friction is generated in this process, and it is usually used for parts with long lengths and higher precision. This method can lead to reduced heat generation and improved physical properties of the part.
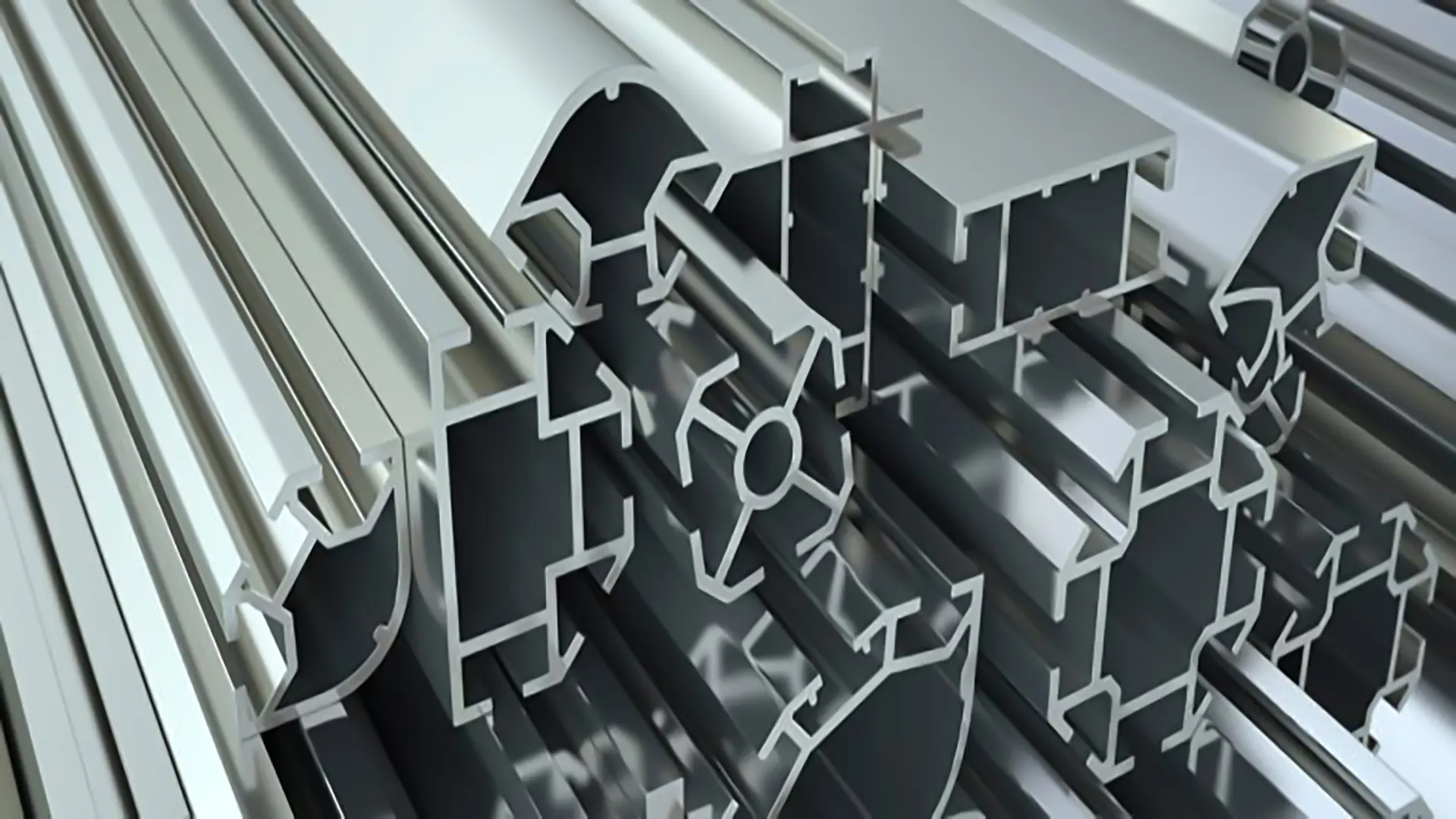

Advantages of extrusion
Production of complex parts: Ability to produce profiles and parts with complex geometries, which might be impossible or difficult with other methods. Use of brittle materials: This method can deform brittle materials that would break under high pressure in other methods. High flexibility: Extrusion can be used for various types of materials, from metals to polymers and ceramics. High production speed: This method, typically due to its continuous or semi-continuous process, can achieve higher production rates in less time.
Applications
The extrusion process is employed in many industries, including the manufacturing of aluminum profiles for windows, the production of metal pipes and rods, automotive parts, electronic components, and even in the fabrication of plastic pipes and industrial ceramics.
